A venomous snake, 60–90 cm long when adult, that occurs throughout Eurasia. It is thick-bodied with a large head, usually with a V or X mark and a zigzag pattern along the back. It feeds on small vertebrates and invertebrates, and is not aggressive, biting only when disturbed or threatened.
In its simplest form, a digital electronic device that performs the operation of addition on two binary digits, the augend and the number to be added, the addend. It is therefore also known as a binary adder. This operation is exemplified by the truth table shown in the diagram, where Σ is the sum and Co is the carry. From this it can be seen that binary addition may generate a carry to subsequent stages.
A full adder has provision for inputs of addend, augend, and a carry bit and is capable of generating sum and carry outputs. These adders may be cascaded when it is desired to add binary words greater than one bit in length by connecting the carry inputs of each stage to the carry output of the previous stage.
A half-adder (see diagram) is an implementation of an adder that has provision only for input of addend and augend bits and is capable of generating sum and carry outputs. These devices cannot directly be cascaded as can full adders but may be made to perform a similar function by including additional logic gating.
See also carry lookahead, parallel adder, serial adder.
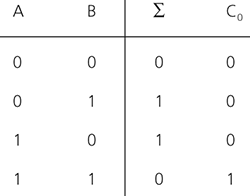
Adder. Truth table of binary half-adder
A circuit in a computer that performs mathematical addition. A full adder contains several identical sections each of which add the corresponding bits of the two numbers to be added together with a carry digit from the preceding section and produce an output corresponding to the sum of the bits and a carry digit for the next section.
A half-adder is a circuit that adds two bits only and produces two outputs; the outputs must be suitably combined in another half-adder in order to produce the correct outputs for all possible combinations of inputs.
If two numbers each consisting of x bits are to be added, a full adder circuit requires 2x inputs to x identical sections and (x + 1) outputs in order to perform the addition.
- isochron
- isochrone
- isochron map
- isochronous
- isoclinal fold
- isocline
- isoclines
- isoclinic chart
- isoconductivity map
- isocost curve
- Isocrates (436–338)
- isocyanate
- isocyanic acid
- isocyanide
- isocyanide test
- isodemographic map
- isodiaphere
- isodynamic line
- ISOE
- isoelectric point
- isoelectronic
- isoenzyme
- isofrigid
- isogal
- isogamy