Any of a number of alloys consisting predominantly of iron with varying proportions of carbon (up to 1.7%) and, in some cases, small quantities of other elements (alloy steels), such as manganese, silicon, chromium, molybdenum, and nickel. Steels containing over 11–12% of chromium are known as stainless steels.
Carbon steels exist in three stable crystalline phases: ferrite has a body-centred cubic crystal, austenite has a face-centred cubic crystal, and cementite has an orthorhombic crystal. Pearlite is a mixture of ferrite and cementite arranged in parallel plates. The phase diagram shows how the phases form at different temperatures and compositions.
Steels are made by the basic-oxygen process (L–D process), which has largely replaced the Bessemer process and the open-hearth process, or in electrical furnaces.
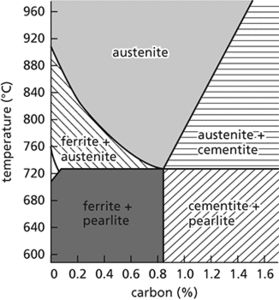
Steel. Phase diagram for steel.
Any of a number of alloys consisting predominantly of iron with varying proportions of carbon (up to 1.7%) and, in some cases, small quantities of other elements (alloy steels), such as manganese, silicon, chromium, molybdenum, and nickel. Steels containing over 11–12% of chromium are known as stainless steels. Adding carbon to iron to make steel can improve some of the properties of iron, e.g. by making it harder.
Carbon steels exist in three stable crystalline phases: ferrite has a body-centred cubic crystal, austenite has a face-centred cubic crystal, and cementite has an orthorhombic crystal. Pearlite is a mixture of ferrite and cementite arranged in parallel plates. The phase diagram shows how the phases form at different temperatures and compositions.
Steels are manufactured by the basic-oxygen process (L-D process), which has largely replaced the Bessemer process and the open-hearth process, or in electrical furnaces.
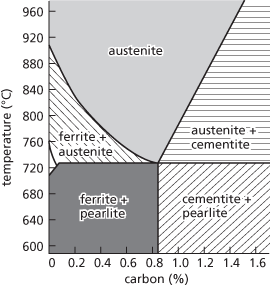
Steel
An alloy of iron used extensively for the fabrication of process vessels, columns, pipes, heat exchangers, ancillary equipment, and supporting structures. Steels contain up to 2.1 per cent carbon and varying amounts of other elements such as manganese, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and silicon. There are many alloy steels with varying properties and used for specific applications. Steel with a chromium content of 11 to 12 per cent is known as stainless steel. Pipes and process vessels are often made from steel due to its high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion. Steel is also used for the support structures for process plant. It is manufactured by the basic-oxygen process, which involves a charge of molten pig iron and scrap being blown with high-pressure oxygen on the surface through a water-cooled lance. See stainless steel.
- shadow bank
- shadow buffer
- shadow economy
- shadow effect
- shadow-mask cathode-ray tube
- shadow price
- shadow prices
- shadow test
- shadow transit
- shadow zone
- Shaftesbury, 3rd Earl of (1671–1713)
- Shaftesbury, Anthony Ashley Cooper, 1st Earl of (1621–83)
- Shaftesbury, Anthony Ashley Cooper, 7th Earl of (1801–85)
- shaft well
- Shah Jahan (1592–1666)
- Shaka (1787–1828)
- shake flask
- shake-out
- shale
- shale gas
- shale line
- shallowing-upward carbonate cycle
- shamal
- shame
- Shamil (1798–1871)