An economic activity by businesses that involves the manufacture of products through the conversion of raw materials, production of goods, or supply of services. See chemical industry.
A sector of the economy in which firms use similar factor inputs to create a group of related products and/or services. The extraction of natural resources, including agriculture, is primary industry; manufacturing is secondary industry; tertiary industry comprises services, including transportation and communication; quaternary industry deals with a range of producer services from banking to retailing to real estate; and quinary industry with consumer services such as education, health care, and government information. With economic development, industry moves from primary industry to progressively less material-oriented activities such as textiles and clothing, until, over time, tertiary industries dominate; the sequence is illustrated in the figure.
The relative dominance of the latter three categories over the former two in many industrialized countries has informed discussions of a post-industrial society, in which Miozzo and Soete (2001) Tech. Forecast. & Soc. 67, 2 identify research and development, design, marketing, distribution, and after-sales maintenance as essential.
Phelps and Ozawa (2003) PHG 27, 5 propose four industrial phases.
Protoindustrial
Industrial
Late industrial
Post-industrial
Sectorial basis
Agriculture-manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing
Services-manufacturing
Division of labour
Intra-firm, intra- and inter-sectorial
Inter-firm and inter-sectorial
Intra- and inter-firm, intra-sectorial
Inter- and inter-firm, inter- and intra-sectorial
Source of accumulation
Exports →domestic
Domestic → exports
Domestic → exports
Exports → domestic
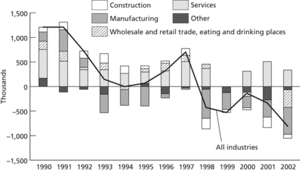
Industry. Industrial change in Japan 1990–2002
Source: Ström, 2005, Soc. Sci. Japan J 8, 2
1. A sector of the economy, in which firms use similar factor inputs to make a group of related products. The Standard Industrial Classification is a partition of industry into sectors and subsectors.
2. A group of sectors, mainly in manufacturing and construction, typically producing physical goods rather than services. The Confederation of British Industry is a UK organization representing firms in these sectors, and the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy is the main UK government department responsible for dealing with them. See also footloose industry; infant industry; nationalized industry; service industry.
- fides quaerens intellectum
- fiducial inference
- fiducial marker
- fiducial point
- fiduciary issue
- fief
- field
- field bus
- field capacity
- field coil
- field current
- field curvature
- field effect
- field-effect transistor
- racemization
- racemose inflorescence
- Race Relations Act (1976)
- rachis
- racial discrimination
- racism
- racking
- rack mounting
- rad
- radar
- radar altimeter