A hollow metal pipe, normally of rectangular cross-section, designed to carry radio waves with little attenuation. A waveguide is commonly used to carry waves from a horn antenna at the focus of a radio telescope to the receiver.
A transmission line that consists of a suitably shaped hollow conductor, which may be filled with a dielectric material, and that is used to guide ultrahigh-frequency electromagnetic waves propagated along its length. The transmitted wave is reflected by the internal walls of the waveguide and the resulting distribution within the guide of the lines of electric and magnetic flux associated with the wave is the transmission mode. At any instant the phase and amplitude of the wave are given by the appropriate propagation coefficient.
For any given transmission mode there is a lower limit to the frequency that may be propagated through the waveguide. This cut-off frequency occurs when the complex propagation coefficient becomes real. The electromagnetic wave is then attenuated exponentially and soon becomes substantially zero. (A short length of waveguide used below cut-off may sometimes be employed as a known attenuator.) The waveguide therefore acts effectively as a high-pass filter. In an ideal (lossless) waveguide, above the cut-off frequency, the propagation coefficient is purely imaginary and no attenuation occurs. In practice however some attenuation of the wave always occurs due to energy dissipation in the guide.
The most common shapes of waveguide are rectangular (Fig. a) and cylindrical; the most common dielectric is air. A cylindrical waveguide is sometimes known as a wave duct; one that contains a solid rod of dielectric is a uniconductor waveguide. If a wide range of frequencies is to be transmitted a ridged waveguide (Fig. b) may be used. The presence of the ridges extends the possible range of frequencies that may be propagated in a particular transmission mode but the attenuation is greater than in the equivalent rectangular waveguide.
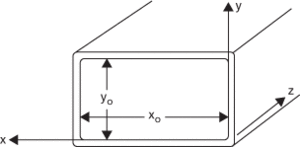
(a) Rectangular waveguide
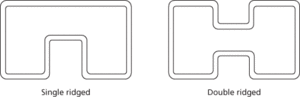
(b) Cross section of ridged waveguides
Electromagnetic waves may be excited in a waveguide by the electric and magnetic fields associated with electromagnetic waves present in another device, such as a cavity resonator or microwave tube. A suitable mount is used to connect the waveguide to the source of radiation in order to achieve the optimum transfer of energy and to excite the desired transmission mode. Energy may also be extracted from a waveguide in a similar manner.
Energy may also be transferred using either a probe to which a voltage is applied or a coil that carries an electric current. The alignment of the exciting probe or coil depends on the desired transmission mode. The probe must be aligned along the direction of lines of electric flux in order to excite the electric field; the coil is aligned so as to excite the desired magnetic field. Energy may be similarly extracted from the waveguide. Probes are also used to examine the distribution of the fields within the waveguide.
A slotted waveguide is one that is provided with nonradiative slots at intervals along its length that allow the insertion of a probe. The presence of the slots affects the distribution of the fields inside the guide, as can junctions (flanges) between sections of a waveguide. Junctions and slots in a guide contribute towards the distributed capacitance of the device and also contribute to the energy dissipation in the guide. A waveguide in which no reflected waves occur at any of the transverse sections is known as a matched waveguide.
Bends in a waveguide are usually made smoothly in order to prevent unwanted reflections. An E-bend is a smooth bend in a waveguide in which the direction of polarization is parallel to the axis (i.e. a horizontally polarized TM wave). An H-bend is a smooth bend in a guide in which the direction of polarization is perpendicular to the axis (i.e. a vertically polarized TE wave). If the direction of polarization has to be changed a special joint, known as a rotator, is used. In a rectangular guide twisting of the guide structure can be used to rotate the plane of polarization.
It is possible to produce local concentrations of electric or magnetic energy within a waveguide by inserting suitably shaped metallic or dielectric pieces. These act essentially as lumped inductances or capacitances. Capacitive elements can be formed from screws; inductive elements can be formed from diaphragms or posts. Either a tuning screw or a waveguide plunger can be used in order to change the impedance of a waveguide. This may be necessary when the impedances of different sections of a waveguide are slightly different. Coupling between two waveguides of different impedances is effected using a suitable waveguide transformer, such as a quarter-wavelength line, for impedance matching. Unwanted frequencies or modes of transmission are eliminated using a waveguide filter. An iris consists of a shaped inductive diaphragm and capacitive screw inserted into a guide to act as a reactance, susceptance, or waveguide filter.
Waveguides are widely used for the transmission of electromagnetic waves. Electromagnetic energy may also be stored by using a section of waveguide short-circuited at each end to form a cavity resonator. A section of coaxial transmission line may also be used. If the length of the section of waveguide or transmission line is h, resonance occurs when
where n is an integer and
λ is the wavelength in free space, λc the wavelength of the waveguide cut-off and ε the relative dielectric constant of the waveguide dielectric. A cavity resonator formed in this way is termed either a waveguide resonator or a coaxial resonator.
http://www.radio-electronics.com/info/antennas/waveguide/waveguide-basics-tutorial.php A tutorial on waveguides
- factorize
- factor loadings
- factor market
- factor mobility
- factor price equalization
- factor price frontier
- factor prices
- factor productivity
- factor(s) of production
- factors of production
- factor space
- factor theorem
- Factor VIII
- Factory Acts
- factory farming
- factory system
- fact-value distinction
- fact/value distinction
- facula
- faculae
- facultative
- facultative anaerobe
- faculty psychology
- FAD
- Fadden, Sir Arthur William (1895–1973)