Denoting a method of supplying an input signal or obtaining an output signal from a circuit in which one side of the input or output is connected to earth. A single-ended amplifier is one in which both the input and output are single-ended. A double-ended input (or output) is one in which neither side of the input (or output) is connected to earth and a differential signal is applied (or obtained).
An example of a circuit that may be used with either single- or double-ended input or output is the simple long-tailed pair (see diagram). When used as an inverter, input B to the base of transistor T2 is earthed to give single-ended input; the output is taken from output P across a load resistor, RL, connected to earth.
The circuit may also be used as a differential amplifier. The difference signal (double-ended) is applied across A and B and the output produced between P and Q. Single-ended output may also be obtained using either P or Q; with Q the output voltage developed is approximately half the value using P, assuming the components are all matched. Differential output may also be obtained using single-ended input.
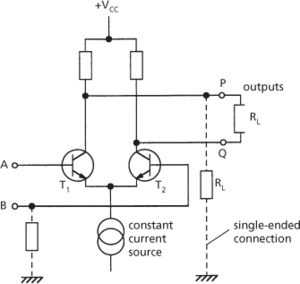
Single-ended and double-ended long-tailed pair
- autothread
- autotomy
- autotransductor
- autotransformer
- autotrophe
- autotrophic nutrition
- autumnal equinox
- Autunian
- autunite
- auxanometer
- auxiliary equation
- auxiliary memory
- auxiliary power unit
- auxiliary reference section
- auxin
- auxin-binding protein
- auxochrome
- availability
- available list
- available nutrients
- available power
- available relief
- available time
- available water
- avalanche