A test of a specified circular distribution, adapted from the Cramér–von Mises test, and introduced by Geoffrey Watson in 1961. Denote the n observations by θ1, θ2,…, θn and write
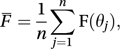 where F(θ) is the probability of a value in the interval (0, θ) according to the null hypothesis. The test statistic is U2, given by
where F(θ) is the probability of a value in the interval (0, θ) according to the null hypothesis. The test statistic is U2, given by 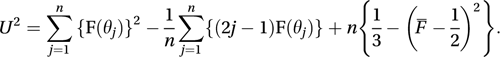 A large value of U2 leads to rejection of the null hypothesis. A transformed version of U2 is provided by U*, given by
A large value of U2 leads to rejection of the null hypothesis. A transformed version of U2 is provided by U*, given by 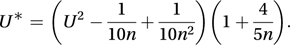 The distribution of U* is approximately independent of n. The upper 10%, 5%, 2.5%, and 1% points of U* are 0.152, 0.187, 0.222, and 0.268, respectively.
The distribution of U* is approximately independent of n. The upper 10%, 5%, 2.5%, and 1% points of U* are 0.152, 0.187, 0.222, and 0.268, respectively.
- Sturtevant, Alfred Henry
- Sturtian
- sturzstrom
- STV
- STW/China
- STX
- Stylasterina
- style
- style guide
- style sheet
- stylized facts
- stylolite
- stylolitization
- S-type asteroid
- styrene
- Störmer, Horst L.
- sub-
- subadditive
- subaerial
- subaltern
- subarachnoid space
- Sub-arctic current
- subarkose
- Subaru Telescope
- Sub-Atlantic