An interface between two layers of different materials (as opposed to a homojunction, which is an interface between two differently doped regions of the same semiconductor). There are several different types of heterojunction: metal–metal, metal–semiconductor, semiconductor–semiconductor, and semiconductor–insulator. In the case of semiconductor–semiconductor heterojunctions the gaps between the energy bands of the two semiconductors are different. Heterojunctions are used to construct transistors, known as heterotransistors, and semiconductor lasers.
An example of a semiconductor–insulator heterojunction is the technologically important silicon–silicon oxide junction, which is a key feature of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) devices, with ‘metal’ referring to the metal electrode in such devices.
Heterojunctions can be manufactured using epitaxy. See also heterostructure.
A junction between dissimilar semiconductor materials. A heterojunction would be typically created during the epitaxial growth process, resulting in a single semiconductor crystal. The different energy band gaps of the two semiconductors in the heterojunction will result in an energy offset between the two conduction and valence bands. The nature of this offset leads to the classification of two fundamental heterojunction types (see diagram). The heterojunctions can be doped, either the same type – isotype heterojunction – or as a p-n junction – anisotype heterojunction. See also heterojunction bipolar transistor; high electron mobility transistor.
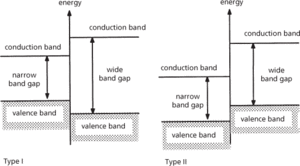
Type I and Type II heterojunctions
- river capture
- river continuum concept
- river grade
- riverine
- river profile
- river restoration
- river-sediment analysis
- River Styles framework
- river terrace
- river training
- river water, major constituents
- Rivest Shamir Adleman Key Encryption Algorithm
- rivet
- rizalite
- Rizal, José (1861–96)
- Rizzio, David (1533–66)
- RJE
- RLC circuit
- RL circuit
- RLL
- RLV
- R magnitude
- RM code
- RME
- RMI