The production of an e.m.f. within a conductor or semiconductor through which a current is flowing when there is a strong transverse magnetic field. The potential difference develops at right angles to both the current and the field. It is caused by the deflection of charge carriers by the field and was first discovered by Edwin Hall (1855–1938) in 1879. The strength of the electric field EH produced is given by the relationship EH=RHjB, where j is the current density, B is the magnetic flux density, and RH is a constant called the Hall coefficient. The value of RH can be shown to be 1/ne, where n is the number of charge carriers per unit volume and e is the electronic charge. The effect is used to investigate the nature of charge carriers in metals and semiconductors, in the Hall probe for the measurement of magnetic fields, and in magnetically operated switching devices. See also quantum Hall effect.
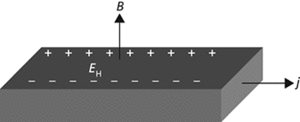
Hall effect.
If current flows in a bar of conductor or semiconductor that is placed in a magnetic field, where the current flow and magnetic field are at right angles, an electric field is set up across the bar, orthogonal to both current flow and magnetic field directions. This effect arises because the charge carriers in the bar experience a force F due to the magnetic field:
where v is the drift velocity of carriers of charge e, and B is the magnetic flux density. Charge carriers are thus forced towards one side of the bar, creating an excess space charge and hence an electric field Ey in the y-direction, across the bar. In equilibrium the forces due to the transverse electric field and the magnetic field are in balance:
or
where J is the current density along the bar, and RH is the Hall coefficient of the material of the bar and is related to the carrier concentration in the bar. The voltage due to this transverse electric field is known as the Hall voltage. Measurement of the Hall voltage enables the Hall coefficient to be found, and hence the type and density of the charge carriers in the bar to be determined:
in an n-type semiconductor,
in a p-type semiconductor,
where n and p are the electron and hole densities, respectively, and r is a function of the detailed charge-scattering mechanisms in the material.
https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/technical-articles/understanding-and-applying-the-hall-effect/ An introduction to the Hall effect, on the All About Circuits website
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AcRCgyComEw A video demonstration of the Hall effect
A strip of metal or semiconductor carrying an electrical current within a strong, transverse, magnetic field develops a potential at right angles to both the current and the field. This forms the basis for some sensitive magnetometers. The effect was discovered by Edwin Hall (1855–1938) in 1879.
- common external tariff
- common factor
- common fraction
- common-gate connection
- Common Gateway Interface
- common gateway interface
- common good
- common-impedance coupling
- common instance
- Common Intermediate Format
- common ion
- common knowledge
- common land
- common law
- common lead
- Common LISP
- common logarithm
- common logarithms
- Common Management Information Protocol
- common market
- common mid-point
- common-mode chokes
- common-mode currents
- common-mode rejection
- common-mode rejection ratio