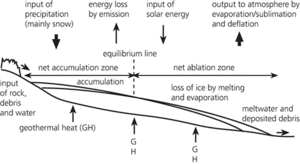
A large mass of ice, resting on or adjacent to a land surface, and typically showing movement. Glaciers may be classified in several ways. The most useful division (as it relates to work done) is based on temperature, and three categories are recognized. In temperate (or warm) glaciers (e.g. those of the Alps) the ice is at pressure melting point throughout, except during winter when the top few metres may be well below 0 °C. Movement is largely by basal slip. Polar (or cold) glaciers (e.g. parts of the Antarctic sheet) have temperatures well below the pressure melting point and movement, which is slow, is largely by internal deformation. Subpolar glaciers (e.g. those of Spitzbergen) have temperate interiors and cold margins and so are composite. The morphological classification is based largely on the size, shape, and position of the ice mass and cirque glaciers, valley glaciers, and piedmont glaciers are among the types recognized.
Glacier
A mass of ice which may be moving, or has moved, overland: when enough ice has accumulated, a glacier will start to move forwards. A glacier may be seen to be the result of a balance between accumulation and ablation. Glaciers are classified by their location (cirque glacier, expanded-foot glacier, valley glacier, niche glacier, piedmont glacier), by their function (diffluent glacier, outlet glacier), or by their basal temperature (cold glacier, warm glacier, polythermal glacier). The glacier balance velocity is the velocity required to maintain the glacier in equilibrium without change to its geometry. Glaciers where the actual and balance velocities are similar are said to be in balance with the current climate, and are unlikely to experience major changes in flow rate unless the climate changes.
- developmental state
- development economics
- development life cycle
- Devensian
- deviance
- deviance information criterion
- deviance residual
- deviant causal chain
- deviation
- deviation distortion
- deviation ratio
- deviatoric stress
- device
- device convergence
- device coordinates
- device driver
- device driver virus
- Deville, Henri Etienne Sainte-Claire
- devil’s staircase
- devitrification
- devolution
- Devolution, War of
- Devonian
- Devonshire, William Cavendish, 4th Duke of (1720–64)
- de Vries cycle