A complex organic compound (a nucleic acid) in living cells that is concerned with protein synthesis. In some viruses, RNA is also the hereditary material. Most RNA is synthesized in the nucleus and then distributed to various parts of the cytoplasm. An RNA molecule consists of a long chain of nucleotides in which the sugar is ribose and the bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil.
There are three main types of RNA:
(1) messenger RNA (mRNA),
(2) transfer RNA (tRNA), and
(3) ribosomal RNA (rRNA), each of which has a different structure and a different function.
For protein synthesis to take place, the coding information in DNA is transferred to complementary mRNA, which carries it to the ribosome, a body consisting of rRNA. Here the coding information is translated into the sequence of amino acids in a protein, each amino acid having been transferred to the ribosome and matched to a codon on mRNA by tRNA. The amino acids are joined together to form protein chains by tRNA. See also genetic code.
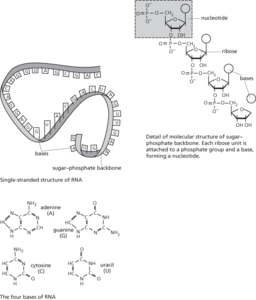
RNA
A complex organic compound (a nucleic acid) in living cells that is concerned with protein synthesis. In some viruses, RNA is also the hereditary material. Most RNA is synthesized in the nucleus and then distributed to various parts of the cytoplasm. An RNA molecule consists of a long chain of nucleotides in which the sugar is ribose and the bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil (see illustration; compare dna). Messenger RNA (mRNA) is responsible for carrying the genetic code transcribed from DNA to specialized sites within the cell (known as ribosomes), where the information is translated into protein composition (see RNA processing; transcription; translation). Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is present in ribosomes; it is single-stranded but helical regions are formed by base pairing within the strand. Transfer RNA (tRNA, soluble RNA, sRNA) is involved in the assembly of amino acids in a polypeptide chain being synthesized at a ribosome. Each tRNA is specific for an amino acid and bears a triplet of bases complementary with a triplet on mRNA (see anticodon; elongation). RNA can associate with proteins to form complexes called ribonucleoproteins. See also antisense RNA; noncoding RNA.
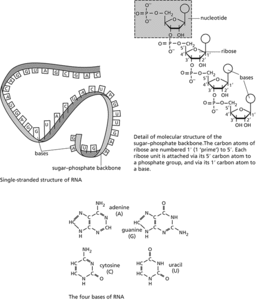
Molecular structure of RNA
http://www.dnaftb.org/21/ Animated account of the roles of RNA in protein synthesis: part of the website DNA from the Beginning
- discrete random variable
- discrete signal
- discrete source
- discrete space
- discrete structure
- discrete symmetry
- discrete system
- discrete time
- discrete-time Markov chain
- discrete variable
- discretion
- discretionary access control
- discretionary policy
- discretionary spending
- discretization
- discretization error
- discriminant
- discriminant analysis
- discriminating monopoly
- discrimination
- discrimination information
- discriminator
- discriminatory
- discriminatory analysis
- disc thermistor