See RTL.
A family of integrated logic circuits that was the first to be developed but is now little used. The input is through a resistor into the base of an inverting transistor. The basic NOR gate is shown overleaf. The output is high (corresponding to a logical 1) only if both the inputs are low (corresponding to a logical 0). If either input is high the transistor conducts and saturates and the voltage at the output is low. RTL circuits tend to be slow low fan-out circuits that are susceptible to noise but the power dissipated is low compared to emitter-coupled, diode-transistor, and transistor-transistor logic circuits.
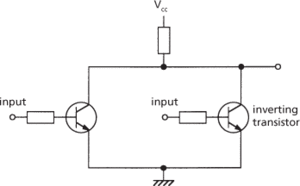
Resistor-transistor logic: two-input NOR gate
- homogeneous polynomial
- homogeneous rotational strain
- homogeneous set of linear equations
- homogeneous(statistics)
- homogeneous strain
- homogenitus
- homogenization
- homogenization temperature
- homograph attack
- homoiotherm
- homoiothermy
- homoiousion
- homojunction
- homoleptic compound
- homological
- homologous
- homologous chromosomes
- homologous series
- homology
- homolytic fission
- homometric structures
- homomorphic image((of a formal language))
- homomorphism
- homomutatus
- homonormativity