An integral transform of the type:
The inverse is:
Fourier transform techniques are used in obtaining information from spectra, especially in NHR and infrared spectroscopy (see Fourier-transform infrared).
The integral transform for an integrable function f on ℝ. The Fourier transform is also denoted by ℱ. The function is the Fourier transform of f. The Fourier inverse is given by See discrete Fourier transform, convolution, Laplace transform.
The mathematical breakdown of a non-repeating phenomenon into its component frequencies. It may be regarded as Fourier analysis applied to a function with an infinite period. The technique is widely used in image processing to reduce the effects of periodic and random errors. It is also needed to convert the outputs from aperture synthesis telescopes and Fourier transform spectrometers into images and spectra respectively.
If f is a function of the real variable x, its Fourier transform F is defined by
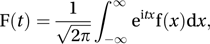 where and t is a real variable. The inverse Fourier transform is given by
where and t is a real variable. The inverse Fourier transform is given by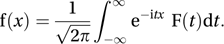
An integral transform of the type:
The inverse is:
Fourier transform techniques are used in obtaining information from spectra, especially in NMR and infrared spectroscopy (see Fourier-transform infrared).
A mathematical operation that analyses an arbitrary waveform into its constituent sinusoids (of different frequencies and amplitudes). This relationship is stated as
where s(t) is the waveform to be decomposed into a sum of sinusoids, S(f) is the Fourier transform of s(t), and i = √−1. An analogous formula gives s(t) in terms of S(f), but with a normalizing factor, 1/2π. Sometimes, for symmetry, the normalizing factor is split between the two relations.The Fourier transform pair, s(t) and S(f), has to be modified before it is amenable to computation on a digital computer. This modified pair, called the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) must approximate as closely as possible the continuous Fourier transform. The continuous time function is approximated by N samples at time intervals T:
The continuous Fourier transform is also approximated by N samples at frequency intervals 1/ NT:Since the N values of time and frequency are related by the continuous Fourier transform, then a discrete relationship can be derived:
The mathematical formulae by which a time function (e.g. a seismic trace) is converted into a frequency-domain function and vice versa. See also fourier analysis; fourier synthesis.
- benzenesulphonic acid
- benzenium ion
- benzil
- benzilic acid rearrangement
- Benz, Karl (1844–1929)
- benzoate
- benzodiazepines
- benzofuran
- benzoic acid
- benzoin
- benzopyrene
- benzoquinone
- benzoylation
- benzoyl chloride
- benzoylecgonine
- benzoyl group
- benzpyrene
- benzvalene
- benzyl alcohol
- benzylamine
- benzyne
- Beowulf cluster
- BepiColombo
- BeppoSAX
- BER