The process of cooling a substance and of maintaining it at a temperature below that of its surroundings. In the domestic refrigerator a cycle of operations equivalent to those of a heat pump is used.
The vapour-compression cycle
In this cycle a volatile liquid refrigerant, such as a fluorocarbon, is pumped through the cooling coils of the evaporator to the ice-making compartment of the refrigerator. Inside these coils the refrigerant evaporates, taking the latent heat required to effect the change of state from the inside of the ice-making compartment, causing the temperature in this compartment to fall. The vapour is then passed to an electrically driven compressor before entering the condenser, where the high-pressure gas is converted back to a liquid. The heat produced by this second change of state is given out, usually at the back of the refrigerator, to the room in which the refrigerator stands. The liquid refrigerant then enters a storage vessel before finally passing through an expansion valve to reduce its pressure prior to beginning the cycle again in the evaporator. This cycle is repeated over and over again until the temperature reaches the desired level (about 1–2°C in the food chamber of a domestic refrigerator and minus 15–18°C in the deep-freeze compartment). The compressor is then switched off, and on again later, by a thermostat to maintain a steady temperature. In order to transfer heat from the cold interior to the warm surroundings without contravening the second law of thermodynamics energy has to be supplied to the cycle by the electric current that drives the compressor.
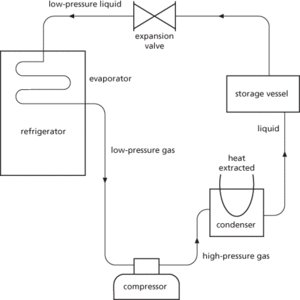
Refrigeration. Vapour-compression cycle.
The vapour-absorption cycle
In this cycle there are no moving parts and energy is supplied as heat either by an electric heater or a gas burner. The refrigerant is usually ammonia, which is liberated from a water solution and moved through the evaporator by a stream of hydrogen gas under pressure. Heat is applied to the generator, raising the ammonia and water vapour to the separator; the ammonia separates from the water and passes to the condenser, where it cools and liquefies, giving off its latent heat to the surroundings. The liquid ammonia is then mixed with hydrogen gas, which carries it through the evaporator and helps in the process of evaporation. Subsequently the hydrogen and ammonia vapour enter the absorber, where the water returned from the separator dissolves the ammonia before returning to the generator.
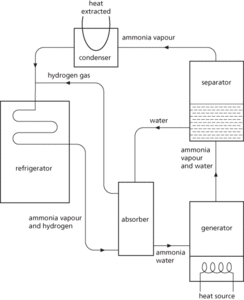
Refrigeration. Vapour-absorption cycle.
Small-scale refrigeration
These two systems account for all domestic and industrial refrigerators including those in ships, trains, and refrigerated lorries. However, small-scale refrigeration is sometimes achieved by means of the Peltier effect at junctions for n-type and p-type semiconductors.
The process of cooling or freezing substances such as foods or process liquids and maintaining them at a temperature below that of their surroundings. The most commonly used refrigeration plants use a vapour compression refrigeration cycle. This consists of a compressor, evaporator, expansion valve, and condenser connected in series. Heat is absorbed by a refrigerant causing it to boil. The vapour is then compressed to an elevated pressure, and then condensed to a liquid releasing the absorbed heat. The liquid is then returned to the low-pressure evaporator through a throttle valve for reuse (see Fig. 51). The ideal cycle can be presented on a temperature-entropy diagram or a pressure-volume diagram. Within the refrigeration process, the coefficient of performance is the ratio of the refrigeration effect to the work input. The vapour absorption cycle is also used in industrial refrigeration systems and involves a refrigerant such as ammonia. Small-scale refrigeration can be achieved using the Peltier effect.
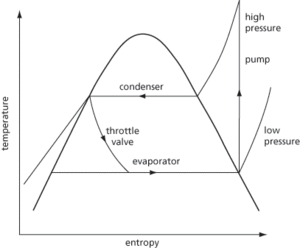
Fig. 51
- microlog
- micromanipulation
- micromanipulator probe
- MicroMAS-2
- micrometeorite
- micrometeoroid impact
- micrometer
- micrometre
- micron
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- micron(symbol: μ)
- micronucleus
- micronutrient
- microorganism
- micropalaeontology
- micropayment
- microperthite
- microphagous
- microphenocryst
- microphone
- microphony
- microphyll
- micropipeline
- micropipette
- micropiracy