The use of part of the output of a system to control its performance. In positive feedback, the output is used to enhance the input; an example is an electronic oscillator, or the howl produced by a loudspeaker that is placed too close to a microphone in the same circuit. A small random noise picked up by the microphone is amplified and reproduced by the loudspeaker. The microphone now picks it up again; it is further amplified, and fed from the speaker to microphone once again. This continues until the system is overloaded. In negative feedback, the output is used to reduce the input. In electronic amplifiers, stability is achieved, and distortion reduced, by using a system in which the input is decremented in proportion as the output increases. A similar negative feedback is used in governors that reduce the fuel supply to an engine as its speed increases.
The output of a system when it is fed back into the system as input. Feedback may be positive or negative. Positive feedback has an additive effect, increasing the system output; negative feedback has a damping effect, tending to stabilize the system.
Response to operator input that indicates that the input has been understood and the desired action accomplished. See also acknowledgment, echoing, prompt.
The process of returning a fraction of the output energy of an energy-converting device to the input. The circuit that transmits the feedback signal to the input is the beta circuit; the circuit containing the active device, which generates the output signal, is the mu circuit.
In the case of an active device, such as a transistor, that introduces a gain A in the absence of feedback, voltage feedback is employed if a fraction β of the output voltage is returned to the input (Fig. a). The effective output voltage is given by
The overall gain of the combination is then
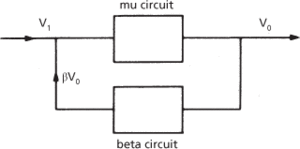
(a) Voltage feedback circuit
If β is negative the feedback voltage opposes the input voltage and the process is termed negative feedback. The overall gain of the device is reduced but there is a corresponding reduction in the amount of noise and distortion in the output. If the term (–βA) is made large compared with unity the overall gain reduces to 1/β and is independent of the elements in the mu circuit. An amplifier operated in this manner is very stable and is independent of minor variations in the operating conditions.
If β is positive the feedback voltage reinforces the input voltage and the process is termed positive feedback. The overall gain of the device is increased and if the factor (–βA) becomes equal to or greater than unity the output voltage becomes independent of any input signal and oscillations occur. The point at which the term (–βA) just becomes unity for any given circuit is termed the singing point. The overall combination can then be considered to have an effective negative resistance (see also oscillator).
Current feedback is a form of feedback in which a fraction of the current output to the load is fed back to the input (Fig. b). The effective output current is given by
and the overall gain is given by
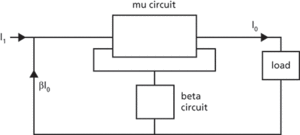
(b) Current feedback circuit
An analysis similar to that of voltage feedback can then be applied.
In a multistage amplifier, feedback may be applied to each individual amplifier stage (local feedback) or across the composite device (multistage feedback). The phase of the feedback at the input is maintained in the correct relationship to the input by introducing a reactance in the feedback circuit. Capacitive feedback uses one or more capacitors and inductive feedback uses a self-inductance or a mutual inductance.
Feedback is also used in control systems when a fraction of the controlled parameter is fed back in order to produce any necessary correcting signals (see feedback control loop).
The use of part of the output of a system to control its performance. In positive feedback, the output is used to enhance the input; in negative feedback, the output is used to reduce the input. Many biological processes rely on negative feedback. As the population of a species expands, so its food supply per individual is diminished; the result is that the population then begins to fall. Many biochemical processes are controlled by feedback inhibition. Feedback mechanisms play an important role in maintaining a state of equilibrium within an organism (see homeostasis).
The response within a system to an action or process. Negative feedback causes the situation to revert to the original; in a river system, erosion is a negative feedback mechanism that restores stream stability by lowering channel gradient and increasing bed material size (Nunally (1985) Env. Manage. 9, 5). Positive feedback causes further change: positive feedbacks involve a move away from an equilibrium state. Perry and Enright (2002) J. Biogeog. 29 note that positive feedback loops between fire and vegetation have degraded tropical and humid forest ecosystems.
- terric horizon
- terrier
- terrigenous
- territoriality
- territorial justice
- territorial seas
- territory
- terroir
- terrorism
- Terror, Reign of
- Terskol Observatory
- Tertiary
- tertiary
- tertiary alcohol
- tertiary amine
- tertiary colour
- tertiary consumer
- tertiary creep
- tertiary industry
- tertiary qualities
- tertiary structure
- tertiary winding
- tertium non datur
- Tertullian (160–c.240)
- Tertullian, Quintus Septimus Florens (ad c.160–c.240)