See discrete Fourier transform.
A numerical method for rapid computation of the coefficients in a finite Fourier transform. The method was introduced in 1965 by Tukey and the American mathematician James W. Cooley. If the (possibly complex) values of a function f(x) are known at N equally spaced points, x0, x1,⋯, xN−1, where xk = 2πk/N for k = 0, 1,⋯, N−1, the coefficients cn are such that
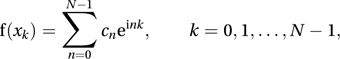 where .
where .
An algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform accurately and efficiently on digital computers. FFT techniques have wide applicability in linear systems, optics, probability theory, quantum physics, antennas, and signal analysis.
See discrete Fourier transform.
An algorithm (e.g. the Cooley–Tukey method) which enables the Fourier transformation of digitized wave-forms to be accomplished more rapidly by computer than would be possible using direct evaluation of the Fourier integral. FFT usually involves iterative techniques. See also fourier analysis; fourier transform.
- thermal tile
- thermal transfer printer
- thermal velocity
- thermal wind
- thermic
- thermionic cathode
- thermionic emission
- thermionic-field emission
- thermionics
- thermionic valve
- thermistor
- thermite
- thermite process
- thermochemistry
- thermochronology
- thermocirque
- thermoclastic
- thermocline
- thermocouple
- thermodynamic cycles
- thermodynamic diagrams
- thermodynamic equilibrium
- thermodynamics
- thermodynamics, laws of
- thermodynamic temperature