The study of the properties of electromagnetic radiation and the way in which it interacts with charged matter in terms of quantum mechanics. The collision of a moving electron with a proton, in this theory, can be visualized by a space–time diagram (Feynman diagram) in which photons are exchanged.
Perturbation-theory calculations using Feynman diagrams enable an agreement between theory and experiment to a greater accuracy than one part in 109 to be obtained. Because of this, QED is the most accurate theory known in physical science. Although many of the effects calculated in QED are very small (about 4 × 10−6 eV), such as the Lamb shift and the magnetic moment of the electron, they are of great significance for demonstrating the physical reality of fluctuations and polarization in the vacuum state. QED is a gauge theory for which the gauge group is Abelian (see group theory).
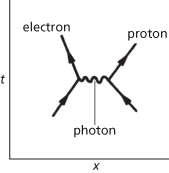
Quantum electrodynamics. An electron–proton collision.
The quantum theory of electromagnetic interactions. In principle, although the whole of chemistry is contained within QED, most problems can be analysed using quantum mechanics. However, a complete analysis of all the energy levels in atoms requires QED. QED is also required to give a complete theory of intermolecular forces and the quantum theory of radiation, particularly the laser. See also Dirac equation.
- grooming
- Grooved Terrain
- grooved terrain
- groove mark
- grosbeak
- Grosch’s law
- gross
- gross domestic capital formation
- gross domestic fixed capital formation
- gross domestic product
- gross drying rate
- gross economic potential
- Grosseteste, Robert (c.1168–1253)
- gross fixed investment
- grossing up
- gross investment
- gross lift-off weight
- gross national income
- gross national product
- gross profit
- gross reproduction rate
- gross trading profit
- grossular
- gross value added
- Grothendieck, Alexander (1928–2014)