The branch of Statistics concerned with the efficient estimation of the unknown parameters in a linear model. Common experimental designs include balanced incomplete blocks, crossover trial, factorial experiments (see factorial design), Latin squares, paired comparisons, randomized blocks, repeated measures, and split plots. In each case a linear model relates the response variable (see regression) to one or more explanatory variables. The results are usually summarized in an ANOVA table.
The analysis of the ANOVA table is affected by the nature of the explanatory variables. For example, if a design compares treatment A with treatment B because these specific treatments are of interest, then they are said to have fixed effects. On the other hand, if treatments A and B have been chosen at random from a population of possible treatments with the intention of attempting to answer the general question ‘Do treatments differ?’, then they are said to have random effects. A design including both random and fixed effects is a mixed effects design.
An example of a random effects model is
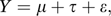
where μ is the fixed overall mean, τ is a random effect (variance σ2t), and ε is a random error (variance σ2). The overall variance for Y is therefore σ2t + σ2 with the proportion due to random effects being σ2t/(σ2t + σ2). This is variously known as the intraclass correlation coefficient (see separate entry for alternative definition) or the intracluster correlation coefficient (a cluster being the set of observations on a particular treatment). This is not a correlation coefficient of the usual form since the bounds are 0 and 1.
If a design is repeated, so that there are two or more observations being made under each experimental condition, then this is called replication and the separate sets of results are called replicates.
In most of the designs mentioned in the first paragraph, the design matrix, X (See multiple regression model) is such that the matrix product X′X is diagonal and the estimators of the model parameters are uncorrelated variables. There are three other general classes of models having desirable properties. Models with A-optimality are such that the trace (see matrix) of (X′X)−1 is minimized. This corresponds to a minimization of the average variance of the parameter estimators. Models with D-optimality are obtained by minimizing the determinant (see matrix) of (X′X)−1, which implies that in this case the covariances of the estimators are also taken into account. Models with E-optimality are obtained by minimizing the largest eigenvalue (see matrix) of (X′X)−1.
A statistical procedure used to evaluate the influence of process variables on the outcome from a process. The purpose is to determine the key information such as a process optimization quickly and cheaply. The simplest approach is to adjust one variable at a time, such as changing the temperature, and evaluating the effect before adjusting another variable. Various protocols have been developed in which combinations of all the important variables can be considered simultaneously. The adjustments follow a defined matrix. A simple approach and early method known as response surface methodology (RSM) was developed by British statistician George Edward Pelham Box, FRS, with K. B. Wilson in 1951. It was designed to explore the relationships between several process variables and one or more response variables. It uses two levels (coded as x = −1 and x = 1) for each process variable such as high and low in a full-factorial design. It involves all combinations of all levels of the variables. For example, in a two-level full factorial experimental design with two variables, there are four treatments. In this case, the number of treatments is equal to 2n. The effects of the two variables and their interactions can be described by the response surface in the form:
Other experimental designs have been developed and involve more than two levels, and also involve the use of replicates used to evaluate the statistical error. Fractional factorial experimental designs use part of the full factorial experimental design and cut down the number of trials needed.
A system of allocating treatments to experimental units so that the effects of the treatments may be estimated by statistical methods. The basic principles of experimental design are replication, i.e. the application of the same treatment to several units, randomization, which ensures that each unit has the same probability of receiving any given treatment, and blocking, i.e. grouping of similar units, each one to receive a different treatment. Factorial designs are used to allow different types of treatment, or factors, to be tested simultaneously. Analysis of variance is used to assess the significance of the treatment effects. See also fractional replication, missing observations.
- jökull
- K
- k
- KA9Q
- Ka band
- kabbala
- Kabir (1440–1518)
- Kadafy, Moamar al
- Kadenyuk, Leonid (1951–2018)
- agnosticism
- Agnostida
- agonic line
- agonist
- agonistic behaviour
- agoraphobia
- AGP
- AGR
- agranulocyte
- agree
- agreement, method of
- agribusiness
- agrichnion
- agric horizon
- Agricola, Georgius
- Agricola, Georgius (1494–1555)