The expected value E(X) of a random variable X is a value that gives the mean value of the distribution. For a discrete random variable X, E(X) = ∑pixi, where pi = Pr(X = xi). For a continuous random variable X,
where f is the probability density function of X. The following laws hold:
(i) E(aX+bY) = aE(X)+bE(Y).
(ii) When X and Y are independent, E(XY) = E(X)E(Y).
(iii) The law of total expectation: for a partition A1, A2, …, An of the sample space
The following is a simple example. Let X be the number obtained when a die is thrown. Let xi = i, for 1 ≤ i ≤ 6. Then , for all i. So .
The expected value of a random variable X, is denoted by E(X) and may be interpreted as the long-term average value of X. In the case of a discrete random variable, taking values x1, x2,…
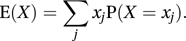 For a continuous random variable with probability density function f,
For a continuous random variable with probability density function f,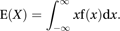 E(X) is often referred to as the expectation of X or as the mean of X. The word ‘expectation’ has been used in this context since the use of ‘expectatio’ by Huygens in his 1657 treatise on the results of playing games of chance: De Ratiociniis in Ludo Aleae.
E(X) is often referred to as the expectation of X or as the mean of X. The word ‘expectation’ has been used in this context since the use of ‘expectatio’ by Huygens in his 1657 treatise on the results of playing games of chance: De Ratiociniis in Ludo Aleae.If g is any function, the expected value of g(X), E[g(X)], is defined by
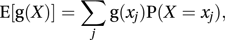 in the case of a discrete random variable, and by
in the case of a discrete random variable, and by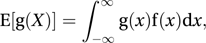 in the case of a continuous random variable. Thus
in the case of a continuous random variable. Thus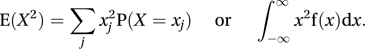 The expected value of a random variable may be thought of as the limiting value of the arithmetic mean of the observed values as the sample size increases. It should be noted that in the case of a discrete random variable the expected value is generally not a possible value. For example, when an unbiased coin is tossed once, the expected value of the number of heads is ½.
The expected value of a random variable may be thought of as the limiting value of the arithmetic mean of the observed values as the sample size increases. It should be noted that in the case of a discrete random variable the expected value is generally not a possible value. For example, when an unbiased coin is tossed once, the expected value of the number of heads is ½.Some random variables (for example, those with a Cauchy distribution) do not have an expected value. There are also discrete random variables without expected values, though this situation can only arise when the set of possible values is infinite and the sum involved is the sum of a series that does not converge. For example, if , for r = 1, 2,…, where , then the expression for E(X) is , and this series diverges to ∞. For the expected values of sums and products of random variables, see expectation algebra.
Given the probability distribution P(x) of a discrete random variable X, the expected value, or the (mathematical) expectation of a function f(X) is defined as
where the sum is taken over all possible values that X can take. For a continuous random variable X with probability distribution function F(x) the expected value of f(X) is defined as
where the integral is taken over all possible values of X. The expected value of X is also referred to as the mean of the distribution of X.
- Brandon
- brand recognition
- Brandreth, Jeremiah
- Brandt, Georg
- Brandt Report
- Brandt, Willy (1913–92)
- Brand, Vance DeVoe (1931– )
- Brandywine, Battle of (11 September 1777)
- brane world
- Brans, Carl Henry
- Brans–Dicke theory
- Brasilsat
- brass
- brassinosteroid
- Brattain, Walter
- Brattain, Walter Houser
- Brauchitsch, Walter von (1881–1948)
- braunerde
- braunite
- Braun, Karl Ferdinand
- Braun, Karl Ferdinand (1850–1918)
- Bravais lattice
- Bravais law
- Bravais rule
- Bray–Curtis distance