A statistic that provides an indication of the extent to which a multiple regression model can be generalized. This is achieved by fitting the model to every subset of n−1 of the n observations, y1, y2,…, yn, of the response variable (see regression). Let be the fitted value for yj based on the model that uses all the observed values except yj. The corresponding residual ε̂−j is given by
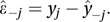 The PRESS statistic is
The PRESS statistic is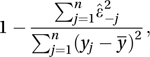 where is the mean of the n observations. The abbreviation PRESS is derived from predicted residual sum of squares. The statistic is an analogue of the R2 statistic (see anova) and values close to 1 are preferable to those close to 0.
where is the mean of the n observations. The abbreviation PRESS is derived from predicted residual sum of squares. The statistic is an analogue of the R2 statistic (see anova) and values close to 1 are preferable to those close to 0.
- Landschaft
- landslide
- Landsteiner, Karl
- land surface process models
- land tenure
- land use zoning
- Landé g factor
- Landé interval rule
- Lanfranc (1010–89)
- Lange, David Russell (1942–2005)
- Lange, Friedrich Albert (1828–75)
- Langerhans cells
- Langevin distribution
- Langevin equation
- Langevin, Paul
- Langevin, Paul (1872–1946)
- Langhian
- Langlands program
- Langlands programme
- Langlands, Robert (1936–)
- Langley, John Newport
- Langley Research Center
- Langley, Samuel Pierpont (1834–1906)
- Langmuir adsorption isotherm
- Langmuir frequency