See logarithm.
See logarithm.
The natural logarithm of a positive real number a is denoted by ln a and defined by
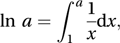 so it is the (signed) area enclosed by the curve y=1/x, the x-axis, and the lines x=1 and x=a. If a>1 then ln a>0, and if a<1 then ln a<0. Also ln 1=0. The natural logarithm is related to the exponential function by exp(ln x)=x for all x>0 and ln{exp(x)}=x for all values of x. It is also referred to as the logarithm to base e. For historical reasons a natural logarithm is sometimes referred to as a Napierian logarithm, after the Scottish mathematician John Napier (1550–1617).
so it is the (signed) area enclosed by the curve y=1/x, the x-axis, and the lines x=1 and x=a. If a>1 then ln a>0, and if a<1 then ln a<0. Also ln 1=0. The natural logarithm is related to the exponential function by exp(ln x)=x for all x>0 and ln{exp(x)}=x for all values of x. It is also referred to as the logarithm to base e. For historical reasons a natural logarithm is sometimes referred to as a Napierian logarithm, after the Scottish mathematician John Napier (1550–1617).
A logarithm that is to the base e (e = 2.718). It is abbreviated to ln or loge. All logarithmic functions are the inverse of a power function.
- phosphorus(V) bromide
- phosphorus(V) chloride
- phosphorus(V) oxide
- phosphorylase
- phosphorylation
- phosphoryl chloride
- phoswich
- phot
- photic zone
- photino
- photo-
- photoacoustic spectroscopy
- photoautotroph
- photoblastic
- photoblog
- photobomb
- photocatalyst
- photocathode
- photocell
- photocentre
- photochemical reaction
- photochemical smog
- photochemistry
- photochromism
- photoconductive cell