A signal representation used in distributed circuits and transmission lines. In such a circuit or network, the voltage and current vary spatially, therefore the indicated impedance also varies with the location of the measurement. To allow an understanding and analysis of the signal flow in the circuit, the signals are represented by power waves, which describe the incident and reflected signals in the transmission line. Given a simple transmission line circuit (see diagram) of characteristic impedance Z0, with Vi and Vr as the incident and reflected voltages at the load,
incident power Pi = |Vi|2/Z0
reflected power Pr = |Vr|2/Z0
power delivered to load PL = (|Vi|2 – |Vr|2)/Z0
load reflection coefficient Γ = (ZL – Z0)/(ZL + Z0)
If this circuit is viewed in terms of power flow, then if the power available from the source is given by
and the power delivered to the load is
then |b|2 can be thought of as the power that is reflected, or scattered by the load. It then follows that
are the incident and reflected power waves, respectively. They have dimensions of √(power). See also scattering parameters.
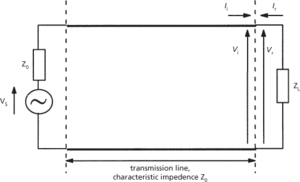
Power waves: transmission line connecting load to source
- lochan
- Lochkovian
- Loch Lomond Stadial
- Loch Lomond stadial
- lock
- lock and key mechanism
- lock-and-key mechanism
- locked zone
- Locke, John (1632–1704)
- Lockheed Martin
- lock-in detector
- locking
- locking-in
- locking-on
- locking relay
- Lockman hole
- lock-on
- lock-out
- lockout
- lockout-tagout
- Lockportian
- lock range
- locks and keys
- Lockyer, (Joseph) Norman (1836–1920)
- Lockyer, Sir Joseph Norman