A sequence of biochemical reduction-oxidation reactions that effects the transfer of electrons through a series of carriers. An electron transport chain, also known as the respiratory chain, forms the final stage of aerobic respiration. It results in the transfer of electrons or hydrogen atoms derived from the Krebs cycle to molecular oxygen, with the formation of water. At the same time it conserves energy from food or light in the form of ATP. The chain comprises a series of carrier molecules that undergo reversible reduction-oxidation reactions, accepting electrons and then donating them to the next carrier in the chain – a process known as electron flow. In the mitochondria, NADH and FADH2, generated by the Krebs cycle, transfer their electrons to a chain including coenzyme Q (see ubiquinone) and a series of cytochromes. This process is coupled to the formation of ATP at three sites along the chain. The ATP is then carried across the mitochondrial membrane in exchange for ADP. An electron transport chain also occurs in photosynthesis.
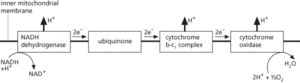
Electron transport chain
A series of molecules that transfers electrons via a sequence of biochemical reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions to effect a stepwise change in free energy. An electron transport chain, also known as a respiratory chain, forms the final stage of cellular respiration. The components of this chain are located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria and consist of multiprotein complexes (labelled I to IV) with tightly bound prosthetic groups (cofactors and coenzymes) essential to catalysing the reactions of the chain. Each component is present in multiple copies in a single mitochondrion. NADH or FADH2, generated by the Krebs cycle, transfer their electrons through a chain of electron carrier molecules, including iron-sulphur proteins, ubiquinone (Q), and a series of cytochromes (cyt), that undergo reversible redox reactions, accepting electrons and then donating them to the next carrier in the chain—a process known as electron flow. Cytochrome oxidase combines electrons and hydrogen ions with oxygen—the final electron acceptor in the chain—to form water (see illustration). This process is coupled to the formation of ATP by the chemiosmotic mechanism (see also oxidative phosphorylation). An electron transport chain also occurs in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts in photosynthesis; the carrier molecules include plastoquinone, plastocyanin, and ferredoxin. See photophosphorylation.
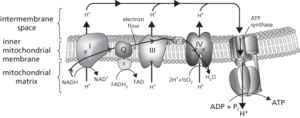
The mitochondrial electron transport chain and chemiosmotic synthesis of ATP
- protonema
- protonephridium
- protonic acid
- proton magnetometer
- proton number
- proton pump
- Proton rocket
- proton–proton reaction
- proto-oncogene
- protoparian suture
- protophloem
- protoplanet
- protoplanetary nebula
- protoplasm
- protoplast
- Protopteridales
- protore
- protostar
- protostome
- protosun
- Prototheria
- prototype
- prototype filter
- prototype theory
- protoxylem