A graphical method used to obtain a straight line from experimental data from enzyme kinetics (see Fig. 18). It involves forming a plot of V/S versus V in which S is the substrate concentration at which the velocity v is observed. The gradient of the line is equal to –Km and the intercept on the y-axis is equal to the maximum velocity V. It is named after Canadian biochemist George Sharp Eadie (1895–1976) and B. H. J Hofstee who developed the plot in 1942 and 1959, respectively. See michaelis–menten kinetics.
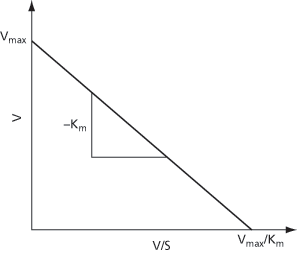
Fig. 18
- peptide
- peptide mapping
- peptide YY
- peptidoglycan
- Pepys, Samuel (1633–1703)
- Pequot War (1637)
- per-
- per accidens
- peralkaline
- peraluminous
- peramorphosis
- per capita income
- per capita real GDP
- per cent
- percentage
- percentage error
- percentage modulation
- percentage point
- percentage yield
- percentile
- percentile life
- perception
- perceptron
- percepts
- Perceval, Spencer (1762–1812)