An object or system in which two separate aspects can be described. For example, in quantum mechanics, the particle and wave nature of both light and electrons is a duality (see complementarity). In the theory of phase transitions, in certain model systems there is a duality in which quantities in the low-temperature phase are related to quantities in the high-temperature phase to give information about the transition point. In projective geometry (the type of geometry associated with perspective), there is duality between straight lines and points. Duality is also a key concept in supersymmetry, particularly in superstring theory. One of the first examples of duality to be identified was the case of electricity and magnetism in electrodynamics. In more general gauge theories there are duality relations between the analogues of electric and magnetic fields. Such dualities have shed light on the issue of quark confinement.
In many areas of mathematics, for a given problem it is possible to describe a dual problem. Solving the dual problem, rather than the original problem, can sometimes be easier, or recognizing the implications of the dual problem can be of benefit. This is particularly true of projective geometry. In a projective plane (see projective space), lines are dual to points, and concurrency is dual to collinearity. Thus ‘two points lie on a unique line’ is dual to ‘two lines meet in a unique point’; proving one result immediately implies the other.
A property of an optimization problem. Duality relates any linear maximization problem to an equivalent minimization problem. For example, with non-negative x-variables and y-variables, the maximum value for A, where
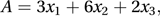 subject to
subject to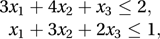 is equal to the minimum value of B, where
is equal to the minimum value of B, where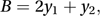 subject to
subject to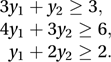
The property exhibited by the laws and rules of set algebra, the propositional calculus, and Boolean algebra that each law or rule has a dual law or rule, constructed by the simultaneous replacement of each occurrence of 0 by 1, 1 by 0, ∨ by ∧, and ∧ by ∨. Such a pair of laws or rules is then said to be self-dual. Thus de Morgan’s laws, for example, are self-dual.
If a law or rule contains the partial ordering ≤ inherent in any lattice, then in obtaining duals this should be replaced by ≥ and vice versa; thus inequalities should be reversed.
Interchangeability of two types of entity in a given system or theory. If two equations that describe the behaviour of two different variables are of the same mathematical form, their solutions will also be identical. The quantities in the two equations that occupy identical positions are known as dual quantities. Duality means that a solution for one of these variables can be derived by systematically interchanging symbols with the solution for the other.
The idea that there are multiple ways of viewing a single issue. More formally, duality applied to optimization theory states that every maximization problem has a dual minimization problem and vice versa. Any problem can be transformed into its dual by interchanging constraints and objectives. In consumer theory the problem of maximizing utility subject to a budget constraint is dual to minimizing expenditure subject to achieving a given level of utility. The use of duality provides alternative ways to represent the solution. For example, the expenditure function and the indirect utility function are equivalent representations of consumer behaviour.
- carrying capacity
- carry lookahead
- carry-over effect
- carry trade
- Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill sequence
- CARS
- Carson, Edward Henry, Baron (1854–1935)
- Carson, Kit (1809–68)
- CART
- Cartan, Elie Joseph
- Carte du Ciel
- cartel
- Carter, Brandon
- Carter, James Earl (1924)
- Carter, Manley Jr (1947–91)
- Cartesian
- Cartesian circle
- Cartesian coordinates
- Cartesian coordinate system
- Cartesian distance
- Cartesian doubt
- Cartesian dualism
- Cartesian ego
- Cartesian plane
- Cartesian product