A movable device used in a cylindrical chamber to transmit a force either onto a fluid in the chamber, such as in a reciprocating pump, or by the expansion of a fluid in the chamber, such as in an internal combustion engine (see Fig. 39). The piston is attached to a connecting rod and crank to transmit or provide power. A piston pump is a type of self-priming positive displacement pump used to transfer and meter fluids using a piston that sweeps into a chamber containing the fluid and displaces it. Check valves are used to ensure that the flow is in the correct direction. The rate of flow is dependent on the frequency of the stroke of the piston and the swept volume. They are capable of generating very high pressures of up to 500 bar, and therefore have a pressure relief valve installed on the delivery side. The sealing of the piston and the check valves are the weak points and they are usually only used for clean fluids of low viscosity, due to the need for quick action by the check valves and the possibility of scoring of the piston.
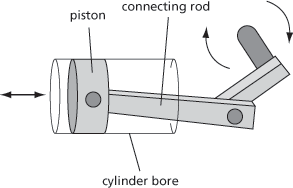
Fig. 39
- anilinium ion
- animal
- animal behaviour
- animal charcoal
- animal geographies
- Animalia
- animal pole
- animal rights
- animal spirits
- animal starch
- animal thought
- anima mundi
- animated GIF
- animation
- anime
- Animikian
- animism
- anion
- anionic detergent
- anionic resin
- Anisian
- anisogamy
- Anisograptidae
- anisometric growth
- anisomyarian