The type of circulatory system that occurs in mammals, in which the blood passes through the heart twice before completing a full circuit of the body (see illustration). Blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs and returns to the heart before being distributed to the other organs and tissues of the body. The heart is divided into two separate compartments to prevent oxygenated blood returning from the lungs from mixing with deoxygenated blood from the other parts of the body. See also pulmonary circulation; systemic circulation. Compare single circulation.
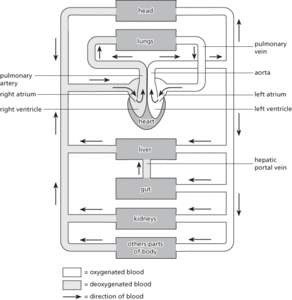
Double circulation in a mammal
- Rafsanjani, Ali Akbar Hashemi (1934–2017)
- raft foundation
- ragged array
- ragged right
- Raglan, FitzRoy James Henry Somerset, 1st Baron (1788–1855)
- ragwort
- Rahman
- rahmonic
- RAID
- rail
- rail transport, Australia
- railway
- railways, history of
- rain
- rainbow
- RainCube
- raindrop
- raindrop erosion
- rainfall intensity
- rainfall run-off
- rain forest
- rainforest
- rain-gauge
- rain-making
- rain print