The genetic material of most living organisms, which is a major constituent of the chromosomes within the cell nucleus and plays a central role in the determination of hereditary characteristics by controlling protein synthesis in cells. DNA is a nucleic acid composed of two chains of nucleotides in which the sugar is deoxyribose and the bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine (compare RNA). The two chains are wound round each other and linked together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary bases to form a spiral ladder-shaped molecule (double helix: see illustration).
When the cell divides, its DNA also replicates in such a way that each of the two daughter molecules is identical to the parent molecule. The hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases on the two strands of the parent molecule break and the strands unwind. Using as building bricks nucleotides present in the nucleus, each strand directs the synthesis of a new one complementary to itself. Replication is initiated, controlled, and stopped by means of polymerase enzymes.
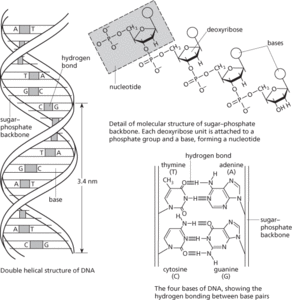
DNA
The genetic material of most living organisms, which is a major constituent of the chromosomes within the cell nucleus and plays a central role in the determination of hereditary characteristics by controlling protein synthesis in cells (see also genetic code). It is also found in chloroplasts and mitochondria (see extranuclear genes; mitochondrial dna). DNA is a nucleic acid composed of two chains of nucleotides in which the sugar is deoxyribose and the bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine (compare rna). The carbon atoms of each deoxyribose unit are numbered 1′ (i.e. 1 ‘prime’) to 5′. Attached to each 5′ carbon atom is a phosphate group, via which a covalent bond forms with the 3′ carbon of the ribose of the adjoining nucleotide. The chains run in opposite directions—they are antiparallel—with 3′ and 5′ chain ends apposed at either end of the molecule. The two chains are wound round each other and linked together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary bases (see base pairing) to form a spiral ladder-shaped molecule (double helix; see also supercoiling). Van der Waals forces between adjacent bases on the same strand also contribute to chain stability. See illustration.
When the cell divides, its DNA also replicates in such a way that each of the two daughter molecules is identical to the parent molecule (see dna replication). Synthesis of DNA from scratch is a key technology of synthetic biology and particularly crucial to fulfilling the potential of DNA as a medium for storing digital data. See also complementary dna.
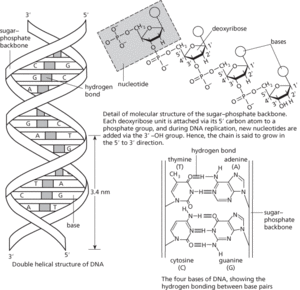
Molecular structure of DNA
http://www.dnaftb.org/ An animated primer on basic aspects of DNA, genes, and heredity, produced for the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
- GEE model
- Geer, Charles de
- Geer, Gerard Jacob de
- Gegenschein
- gegenschein
- Gehan, Edmund Alpheus (1931– )
- Gehan test
- gehlenite
- Geiger counter
- Geiger, Hans Wilhelm
- Geiger, Hans Wilhelm (1882–1945)
- Geiger–Müller counter
- Geikie, Archibald (1835–1924)
- Geissler tube
- Geist
- gel
- Gelasian
- gelatin(e)
- gel electrophoresis
- gel filtration
- gel-filtration
- Gelfond-Schneider theorem
- gelifluction
- gelifraction
- gelignite