The discrete Fourier transform of a vector x = (x0, x1,…, xn−1) is the vector y = (y0, y1,…, yn−1) obtained by calculating for each k = 0, 1,…, n−1 where
This involves a large number of calculations, but the number can be reduced by using an algorithm called the fast Fourier transform.
http://www.jhu.edu/signals/fourier2/index.html A discrete Fourier transform tool in which choosing different options from the signal menu illustrates a number of signals and the approximating function using a specified number of Fourier coefficients.
See Fourier transform.
A mathematical method of analysing discrete or sampled data signals to determine the frequency spectrum. The DFT is equivalent to the Fourier transform for discrete signals and is given by
where x(n) is the discrete signal to be analysed, X(m) is the resulting discrete frequency spectrum, N is the number of x(n) samples taken, and exp indicates the exponential function.
A sampled function of time is shown in Fig. a and its discrete Fourier transform spectrum in Fig. b. The time function is sampled at N points separated by an increment T over an interval tp = NT to create a discrete function x(n). The resulting spectrum X(m) is periodic with a period fs = 1/T, and contains N components within one period with spacing between components F = 1/tp. If x(n) is a real function, only half or N/2 of the spectral components are unique. The integers n and m represent the time and frequency integers that identify the locations in the sequence of the time sample (t = nT) and the frequency components (f = mF).
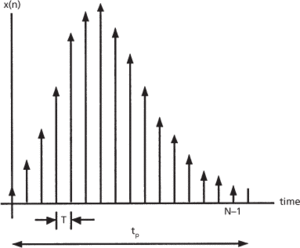
(a) Discrete signal x(n)
A careful investigation of the DFT function shows that many of the multiplication operations are repeated. Algorithms can be devised that exploit this repetition to speed up the transformation by reducing the number of computations required. These high-speed algorithms are known as the fast Fourier transforms (FFT). The use of FFT analysis does however have a number of sources of error. These include aliasing, leakage, and the picket-fence effect. Leakage is an undesirable harmonic distortion that occurs when the time series is not periodic in the sampling interval. The picket-fence effect is due to the frequency response of a finite-length DFT. The DFT can be thought of as a set of narrow band-pass filters whose centre frequencies are located at nfo (where n = 0,1,2,3,… N–1, fo is the sampling frequency, and N the number of samples), as shown in Fig. c. It can be seen that any input signal x(t) coincident with a frequency nfo will be transformed without distortion. However, the frequency components of x(t) at noninteger multiples of fo will be transformed with distortion.
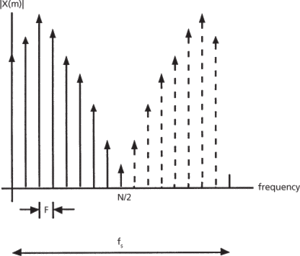
(b) Discrete Fourier transform spectrum X(m)
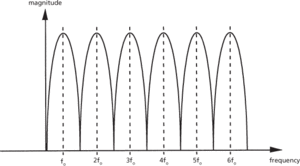
(c) Finite-length DFT response
- cobaltite
- cobalt steel
- cobalt thiocyanate test
- Cobbett, William (1763–1835)
- cobble
- Cobb–Douglas function
- Cobden, Richard (1804–65)
- COBE
- Coble creep
- COBOL
- Cobol
- cobra
- cobranding
- cobweb
- cobweb diagram
- cobweb plot
- COCA
- cocaine
- coccolithophorids
- coccoliths
- coccus
- coccyx
- cochannel interference
- cochannel rejection
- Cochin China