1. A homogeneous part of a heterogeneous system that is separated from other parts by a distinguishable boundary. A mixture of ice and water is a two-phase system. A solution of salt in water is a single-phase system.
2. A description of the stage that a periodic motion has reached, usually by comparison with another such motion of the same frequency. Two varying quantities are said to be in phase if their maximum and minimum values occur at the same instants; otherwise, there is said to be a phase difference. See also phase angle.
3. One of the circuits in an electrical system or device in which there are two or more alternating currents that are not in phase with each other. In a three-phase system the displacement between the currents is one third of a period.
4. See phases of the moon.
Suppose that x = Asin(ωt + α), where A > 0, ω and α are constants. This may, for example, give the displacement x of a particle, moving in a line, at time t. The particle is thus oscillating about the origin. The constant α is the phase. Two particles oscillating like this with the same amplitude and period but with different phases are executing the same motion apart from a shift in time.
1. The proportion of the visible disk of the Moon or a planet that is illuminated as seen from Earth.
2. A measure of position along a cyclically varying quantity, such as a wave or a periodic vibration. Phase is measured as an angle, where one complete cycle is equivalent to a phase of 360° (or 2π radians), or occasionally as a number between 0.0 and 1.0. Two or more waves of the same frequency are said to be in phase when their maxima and minima occur at the same instants. Otherwise, they are said to be out of phase, or to have a phase difference. If their phases differ by exactly 180° they are said to be in antiphase.
In a space mission, any of its predefined periods. An example is the launch and early orbit phase. A fly-by has an observatory phase, far encounter phase, near encounter phase, and post encounter phase.
The apparent shape of the Moon or a planet when all or part of its illuminated hemisphere is facing the Earth.
As the Moon orbits the Earth its appearance from Earth changes as different amounts of its surface are illuminated by the Sun. During one orbit of the Earth (29.5 days, a lunar month) the Moon undergoes a full cycle of phases from new, to first quarter, to full, to last quarter.
The Moon does not reflect sunlight onto the Earth when it is between the Earth and the Sun, and the Moon is not seen. This is the new Moon phase. As the Moon orbits the Earth, part of the Moon reflects sunlight onto the Earth and a crescent is seen, starting from the right-hand side of the Moon. This is the waxing crescent phase. The half Moon phase occurs when half of the Moon's disc is illuminated as seen from Earth. As the Moon continues its orbit, gradually more of the Moon's surface becomes illuminated. At the waxing gibbous phase, three-quarters of the Moon's disc is visible. The full Moon phase occurs when the Earth is between the Moon and the Sun, and the Moon's disc is fully illuminated.
After the full Moon, gradually less of the Moon’s surface is illuminated as it continues its orbit. It passes through the waning gibbous phase where three-quarters of its disc is visible, to the third quarter where half is seen, followed by the waning crescent, and finally the new Moon phase again.
The planets whose orbits lie within that of the Earth can also undergo a full cycle of phases, as can an asteroid passing inside the Earth’s orbit.
Mars can appear gibbous at quadrature (when it is at right angles to the Sun). The gibbous appearance of Jupiter is barely noticeable.
http://tycho.usno.navy.mil/vphase.html Image display of the current phase of the Moon, updated every four hours. You can also find the Moon phase for any date and time between ad 1800 and ad 2199.
1. The form of a substance, such as plasma, gas, liquid, or solid.
2. The stage that a periodic (wave) motion has reached in comparison with another motion with the same frequency. If the maximum and minimum values of two fluctuating values occur at the same moment they are said to be in phase; if not, there is said to be a phase difference between them.
3. A part of a system that is separated by a boundary from other parts of the same system; a mixture of ice and water is a two-phase system.
4. The appearance of the Moon, in terms of the proportion of its disc that is illuminated.
A homogeneous part of a heterogeneous system that is separated from other parts by a distinguishable boundary. A mixture of ice and water is a two-phase system. A solution of salt in water is a single-phase system.
A state of matter being either solid, liquid, or gas. Single-phase flow is the flow of a substance or mixtures of substances of the same phase. Multiphase flow involves a substance or a mixture of substance of different phases. A refrigerant in the evaporator in a refrigeration cycle is an example of multiphase flow involving a liquid and a vapour.
(of a regularly recurring (periodic) quantity) The stage or state of development of the quantity. It can be expressed, in the form of an angle, as the fraction of a cycle of the periodic quantity that has been completed, with respect to a fixed datum point. Two sinusoidally varying quantities of the same frequency can be in phase (reaching corresponding phases at the same time) or out of phase. In the latter case the difference in phase—the phase difference—is usually expressed as an angle.
1. The stage or state of development of a regularly recurring quantity; it is the fraction of the period that has elapsed with respect to a fixed datum point.
The amplitude variations of a sinusoidally varying quantity are similar to simple harmonic motion; such a quantity may be represented as a rotating vector OA (see diagram) of length equal to the maximum amplitude and rotating through an angle 2π during the period, T, of the waveform. The vector has an angular velocity, ω, equal to 2π/T and related to the frequency, f, of the waveform by
The phase of the quantity OA with respect to another quantity, represented by the vector OB, is given by the angle, ϕ, between them (see diagram). This is the phase angle (see also phase difference), which is constant if the two quantities have the same frequency.
Particles in a travelling wavefront moving in the same direction with the same relative displacement are said to be in the same phase of vibration. The wavelength is equal to the distance travelled between two points, in the direction of propagation of a wavefront, at which the same phase recurs.
Periodic quantities that have the same frequency and wave shape and that reach corresponding values simultaneously are said to be in phase; otherwise they are out of phase.
2. One of the separate circuits or windings of a polyphase system or apparatus.
3. One of the lines or terminals of a polyphase system or apparatus.
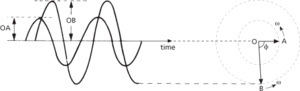
Phase angle ϕ between two quantities of the same frequency
1. An individually distinct and homogeneous part of a system. For example, liquid water and water vapour are each single phases; a mixture of the two constitutes a two-phase system. Similarly minerals crystallizing from a melt form separate phases within it. A ‘phase boundary’ is the line marking the contact between two constituent or liquid phases.
2. A short unit of time, or an episode of development or change, usually within the context of a longer period. The term has been used informally (see informal) in this sense in many branches of the Earth sciences, e.g. ‘a phase of igneous activity’, or ‘a cold phase’ during a generally warmer period.
- fallback
- fall forward
- fallibilism
- falling dune
- falling film evaporator
- falling head permeameter
- falling-rate drying
- falling stage systems tract
- falling star
- fallopian tube
- fall-out
- fallout
- fall over
- fallowing
- falls
- fall-stripes
- fall time
- false
- false acceptance
- false acceptance rate
- false body
- false cirrus
- false colour
- false consciousness
- False Cross