An electronic device with two electrodes. In the obsolescent thermionic diode a heated cathode emits electrons, which flow across the intervening vacuum to the anode when a positive potential is applied to it. The device permits flow of current in one direction only as a negative potential applied to the anode repels the electrons. This property of diodes was made use of in the first thermionic radios, in which the diode was used to demodulate the transmitted signal (see modulation). In the semiconductor diode, a p−n junction performs a similar function. The forward current increases with increasing potential difference whereas the reverse current is very small indeed. See semiconductor; transistor.
An electronic device, generally of semiconductor material, that has two terminals and is capable of allowing current flow in one direction only. The terminals are called the anode and cathode. The diode presents a very low (high) impedance when a forward bias (reverse bias) is applied.
Any electronic device that has only two electrodes. There are several different types of diode, their voltage characteristics determining their application. Diodes are most commonly used as rectifiers; those used for other purposes have special names.
The semiconductor diode consists of a simple p-n junction. Current flows when a forward bias is applied to the diode (see diode forward voltage) and increases exponentially (see diagram). A straight-line approximation of this forward characteristic allows a resistance value (the forward slope resistance) to be calculated from the slope of the straight line. Reverse bias produces only a very small leakage current until breakdown occurs. The now obsolete vacuum or valve diode is a thermionic valve that has an anode and cathode and also passes current only in the forward direction.
See also IMPATT diode; light-emitting diode; photodiode; PIN diode; tunnel diode; varactor; Zener diode.
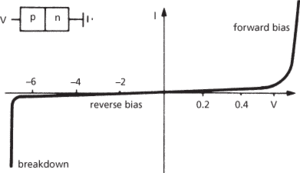
I–V characteristic for semiconductor diode
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/diodes An introduction to diodes, on the sparkfun website