A digraph (or directed graph) consists of a number of vertices, some of which are joined by arcs, where an arc, or directed edge or arrow, joins one vertex to another and has an arrow on it to indicate its direction. The arc from the vertex u to the vertex v may be denoted by the ordered pair (u, v). The digraph with vertices u, v, w, x and arcs (u, v), (u, w), (v, u), (w, v), (w, x) is shown in the first figure.
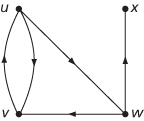
directed graph
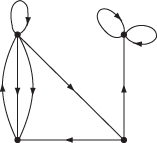
directed multigraph
As with graphs there may be multiple arcs and loops, as shown in the second figure.
See graph.
Short for directed graph. See graph.
- lapilli-tuff
- lapis lazuli
- lapiés
- Laplace distribution
- Laplace equation
- Laplace expansion
- Laplace, Marquis Pierre-Simon (1749–1827)
- Laplace, Marquis Pierre Simon de
- Laplace operator(symbol: ▿2)
- Laplace, Pierre Simon (1749–1827)
- Laplace, Pierre Simon de (1749–1827)
- Laplace, Pierre Simon, Marquis de (1749–1827)
- Laplace, Pierre‐Simon, Marquis de (1749–1827)
- Laplace transform
- Laplace’s correction
- Laplace’s equation
- Laplacian
- Laplacian operator
- Laplacian plane
- Laporte selection rule
- lapout
- lappets
- lapping
- lapse rate
- lapse time