The electronic hardware used in the control of processes that converts a digital signal to an analogue signal such as electrical voltage or current.
See D/A converter.
A device/circuit/IC that converts a discrete binary signal into a continuous analogue signal. A simple DAC can be built up from a series of weighted resistors. Taking a 4-bit binary word, B = b3b2b1b0, the most significant bit (b3) is connected to a resistor of value 2R, bit b2 to a 4R resistor, b1 to an 8R resistor, and so on. The value of the resistor doubles for each less-significant bit. If any bit is at logical 1, a voltage is applied across its resistor and a current inversely proportional to the resistor flows. An operational amplifier circuit can be used to sum the currents and produce a voltage proportional to the total current flowing. The magnitude of the voltage will therefore be directly proportional to the value of the binary number B.
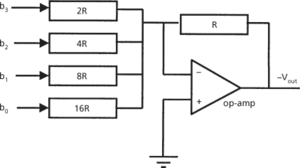
4-bit digital-to-analogue converter
- alcrete
- Alcuin (c.735–804)
- Alcyone
- alcázar
- Aldebaran
- aldehydes
- Alderamin
- Alder, Kurt
- alderman
- Aldermaston
- Aldingan
- aldohexose
- aldol
- aldol reaction
- aldose
- aldosterone
- aldoximes
- Aldrin, Buzz (1930– )
- aleatory variable
- Alemanno, Yohanan ben Isaac (4– after 1503)
- Alembert, Jean Le Rond d'
- aleph
- aleph null
- aleph-null
- alert box