See aberration.
False colour in a refracting optical system, arising because light of different wavelengths is refracted by different amounts. The most common example is the coloured fringes that appear round images produced by a simple lens. Red light is refracted less than blue light, so the red focus lies farther from a lens than the blue focus. An image which is in focus in yellow light will therefore have a red fringe. The longer the focal ratio of a lens, the less chromatic aberration it will show. Early telescopes were made with very long focal ratios for this reason. The achromatic lens was invented to overcome chromatic aberration.
chromatic aberration:
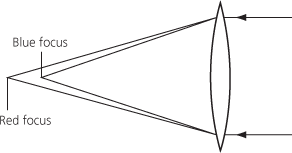
A lens brings blue light to a shorter focus than red light.
- inductive reactance
- inductive tuning
- inductor
- indulgence
- induration
- Indus
- Indus civilization
- indusium
- industrial action
- industrial cluster
- industrial concentration
- industrial democracy
- industrial dispute
- industrial district
- industrial diversification
- industrial economics
- industrial espionage
- industrial fermenter
- industrial geography
- industrial inertia
- industrialization
- industrial licensing
- industrial location policy
- industrial location theory
- industrial melanism