A quadrilateral in which (i) both pairs of opposite sides are parallel and (ii) the lengths of opposite sides are equal. Either property, (i) or (ii), in fact implies the other. The area of a parallelogram equals ‘base times height’. That is to say, if one pair of parallel sides, of length b, are a distance h apart, the area equals bh. Alternatively, if the other pair of sides have length a and θ is the angle between adjacent sides, the area equals absinθ, so the area also equals |a×b|, the magnitude of the vector product of the sides as vectors.
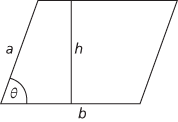
A parallelogram
- nuclear power
- nuclear power plant
- nuclear-precession magnetometer
- nuclear reaction
- nuclear reactor
- nuclear stability
- Nuclear Test-Ban Treaty (1963)
- zeolite facies
- zeolites
- zephyr
- Zeppelin, Ferdinand Adolf Heinrich August, Count von (1838–1917)
- zepto-
- Zermelo, Ernst (1871–1953)
- Zermelo-Fraenkel axioms
- Zermelo-Fraenkel set theory
- Zermelo-König paradox
- Zernike, Frits
- zero
- zero-address instruction
- zero-age horizontal branch
- zero-age main sequence
- zero-base budgeting
- zero coupon bond
- zero crossing
- zero-crossing detector